Types of Agency Relationships
An agency relationship is engaged when an agent agrees to act in the best interest of a client (on their behalf) and represent them when dealing with another party. An agency relationship requires that the agent provide a "fiduciary duty" to the client to act loyally and obediently, and this means placing clients’ interests over agents' interests, being honest and acting in good faith while avoiding self-dealing and other conflicts of interest.
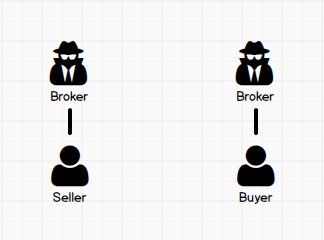
Single AgencyA Broker or Agent represents the interests of the one party in Buying or Selling only.
|
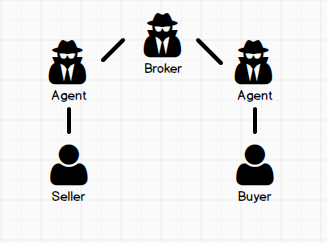
Designated AgencyA Broker designates one Agent to represent the Buyer and a different Agent (under the same brokerage) to represent the Seller.
|
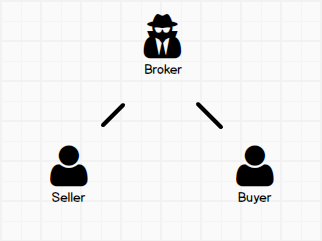
Dual AgencyA single Broker or Agent represents both Buyer and Seller typically in a limited agency relationship, not representing the best interests of either party.
|
|
|
|
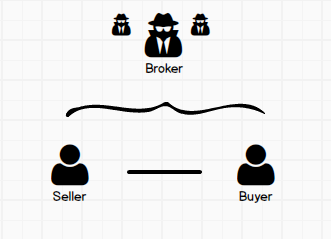
Transaction BrokerageOne Agent or two Agents in the same brokerage provide service to either or both Buyer and Seller, in a non-agency relationship, owing no fiduciary duties to either party.
|
Limited or MinisterialA listing Broker provides limited services to an unrepresented buyer.
|
Sub Agency*One Broker represents the Seller in an agency relationship. "Selling agents" who work with buyers are "subagents" of the listing broker and actually represent the Seller. Buyers are unrepresented. * Rarely Used anymore due to lawsuits
|